Asian Ginseng: Panax comes from the Greek word panacea, meaning cure-all. Ginseng will not cure everything, however it will increase your overall vitality and your physical and mental performance...
Common Names: Asian Ginseng, Korean Ginseng, ren shen ("man root")
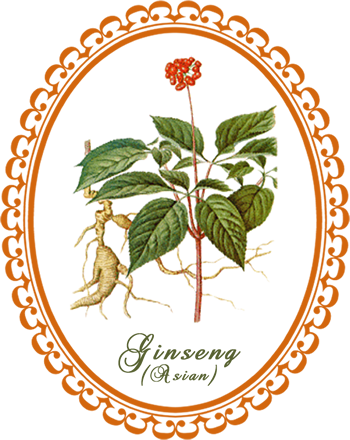
Botanical Name: Panax ginseng
Family: Araliaceae
Plant Type: Hardy perennial
Parts Used: Roots
Asian ginseng is a native of Manchuria and is extensively cultivated there and in nearby Siberia, Korea, and Japan.
Description: Ginseng is a slow-growing perennial that each year produces a single stem from a short rhizome (underground stem) attached to a fleshy, light tan, gnarled root. The stem gives rise to several oval, toothed leaflets and a single cluster of small white flowers. Each flower develops into a fleshy, bright red fruit.
Cultivation: Ginseng likes rich, well-drained loam with a pH of 5.0 to 6.5 in shade. Sow ripe seeds; keep in greenhouse for first winter. Or separate rhizome or "neck" of older plants from roots and replant in spring.
Harvesting: Harvest roots in autumn once the plants are six years old. Use fresh, or dry.
Tip: if you want to use ginseng, use only the root, which can be obtained from a Chinese herbalist shop. Since there are no trade or government standards for ginseng preparations, a "ginseng" capsule, tablet or extract may contain little or no ginseng at all.
Herbal Healing with Asian Ginseng
Medicinal Actions: Adaptogen
Medicinal Uses: Ginseng on the whole is a muscular, masculine herb; it is a well-known yang stimulant. It is an adaptogen, strengthening the whole body by increasing the efficiency of the endocrine, metabolic, circulatory and digestive systems. It acts upon the body by increasing numbers of oxygen-carrying red blood cells and immune-strengthening white blood cells, and eliminating toxins. Ginseng is used to treat exhaustion, depression, and debility. Ginseng can help prevent, but not cure, infections once you have them. It is understandable that ginseng is almost always prescribed with other herbs when it is used for treating specific conditions, since it is not meant to cure the illness by itself, but rather to strengthen the body and help the other herbs do their work.
Contraindications:
- Ginseng is not suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding women, or if you are trying to conceive.
- Younger people should not take it for more than six weeks at a time as it can be too stimulating.
Body Care with Asian Ginseng
- To enhance physical endurance, take 2 or 3 size 00 capsules ginseng root powder three times daily, as required.
- To speed up recovery from a cold, take 1 teaspoon ginseng tincture three times daily until you are better.
Tincture: 20 g (3/4 oz) dried or 40 g (1 -1/2 oz) fresh ginseng root in 1 litre (4 cups) vodka-water mix.
Source: The Essential Herbs Handbook by Lesley Bremness
Panax ginseng Asian Ginseng (root)
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine Panax Ginseng promotes Yang energy, improves circulation, increases blood supply, revitalizes and aids recovery from weakness after illness, and stimulates the body. Panax Ginseng is available in four forms:
The form called fresh ginseng is the raw product.
The form called white ginseng (WG) is fresh ginseng which has been dried. It is grown for four to six years, and then peeled and dried to reduce the water content to 12% or less. White Ginseng is air dried in the sun and may contain less of the therapeutic constituents. It is thought by some that enzymes contained in the root break down these constituents in the process of drying. Drying in the sun bleaches the root to a yellowish-white color.
The form called red ginseng (RG) is harvested after six years, is not peeled and is steam-cured at standard boiling temperatures of 100 degrees Celsius, thereby giving them a glossy reddish-brown coloring. Steaming the root is thought to change its biochemical composition and also to prevent the breakdown of the active ingredients. The roots are then dried. RG is more common as herbal medicine than WG.
The form called sun ginseng (SG) is created from a heat processing method which increases ginsenoside components by steaming white ginseng at a higher temperature than red ginseng. The herb is steamed for three hours at 120 degrees C. Research has shown that SG has increased nitric oxide, superoxide, hydroxyl radical and peroxynitrite scavenging activities compared with conventionally processed RG or WG. The increased steaming temperature produces an optimal amount of biological activity due to its ability to amplify specific ginsenosides.
If you appreciate the information provided,
please help keep this website running. Blessings!
© 2008-2025 aromaworx.ca. All rights reserved.

