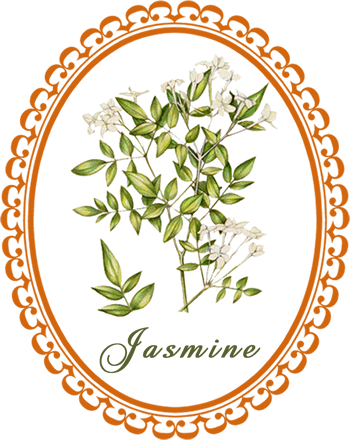
Jasmine: known as "Queen of the Night", jasmine is planted around courtyards, verandas and windows for its intoxicating evening perfume ...
Common Names: Jasmine, Jessamin
Botanical Name: Jasminum officinale
Family: Oleaceae
Plant Type: Evergreen vine, but can be trained as a shrub
Parts Used: Flowers
Flowering: Summer or spring, usually six months after planting.
Jasmine is believed to have originated in the Himalayas in western China.
Description: Jasmine shrubs reach to a height of 10-15 feet, growing approximately 12-24 inches per year. Jasmine leaves are either evergreen or deciduous. A Jasmine leaf is arranged in opposite in most species, leaf shape is simple, trifoliate or pinnate with 5-9 leaflets, each up to two and half inches long. The Jasmine stems are slender, trailing, green, glaborous, angled, almost 4-sided. Most of the Jasmine species bear white flowers, which are about 1 inch in size.
Cultivation: Jasmine is a perennial shrub hardy to zone 7. They grow best in light, well-drained soil in full sun to part shade with high levels of light and humidity.
Harvesting: Pick summer flowers before dawn. Use fresh (for the best scent), or dry.
Jasmine Magick
Love. Money. Prophetic Dreams.
Gender: Female
Planet: Moon
Element: Water
Jasmine will help deepen your meditations and your spiritual connection.
The smell from the flowers will enhance your dream life and help you develop new ideas.
Plant jasmine on the south side of your property to provide protection for your home and family.
Growing jasmine in your home will attract abundance and fill your life with a sense of peace and love.
Herbal Healing with Jasmine
Medicinal Actions: Analgesic, antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiseptic, antispasmodic, antistress, aphrodisiac, calmative, carminative, cicatrizant, decongestant, emollient, euphoriant, expectorant, galactagogue, moisturizer (skin), rejuvenator (skin), sedative, stimulant (uterine contractions), tonic (female reproductive system), uplifting
Medicinal Uses: In China the flowers of J. officinale var. grandiflorum are used to treat hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and dysentery. The flowers of J. sambac are used for conjunctivitis, dysentery, skin ulcers and tumours. The root is used for insomnia, headaches, and pain due to dislocated joints and rheumatism.
Body Care with Jasmine
- To rejuvenate the skin, apply jasmine skin gel daily.
To relieve aching muscles or rheumatic pain, hold a compress made with single-strength jasmine flower infusion against the affected area.
Skin Gel: Stir 2 drops jasmine essential oil into 2 tablespoons aloe vera gel. Scoop into a small, clean jar, seal and refrigerate for up to one month.
Single-strength infusion: 1 teaspoon dried or 2 teaspoons fresh jasmine flowers in 1 cup just-boiled water.
Source: The Essential Herbs Handbook by Lesley Bremness
If you appreciate the information provided,
please help keep this website running. Blessings!
© 2008-2025 aromaworx.ca. All rights reserved.

